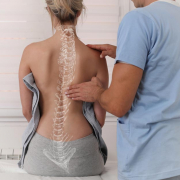
Scoliosis and back pain: physical activity is the best prevention
In the world’s richest countries, low back pain is so common that it has become one of the leading causes of disability and healthcare expenditure. Back pain in children should be taken seriously as it can reduce the amount of physical exercise they get, result in absences from school, and limit them in their everyday activities.
These brief opening remarks prompt a series of questions that our physiotherapist, Martina Poggio, here tries to answer in the light of the latest published data regarding a possible link with adolescent scoliosis.
How prevalent is low back pain in children and adolescents?
In recent decades, a high prevalence (39.9%) of low back pain has been found in children and adolescents: one study found back pain to be associated with age (>12 years), a family history of the condition, spending more than two hours a day studying or watching TV, having an uncomfortable desk at school, suffering from generalised pain, and sleep problems. Evidence on the impact of heavy backpacks is conflicting.2
How common is idiopathic scoliosis among adolescents with back pain?
Aetiologically speaking (in other words, when examining the possible causes of the condition), one retrospective study, conducted in almost 2000 patients under the age of 21 years, found the following underlying conditions: scoliosis, followed by Scheuermann’s disease and spondylolisthesis.1 However, since the role of spinal deformities in back pain is unclear, we reviewed recent literature on the association between pain and the most common adolescent spinal deformity, i.e., idiopathic scoliosis, which affects 1 to 3% of adolescents. Although idiopathic scoliosis was considered painless condition until a few decades ago, more recently patients seem to show a higher prevalence of back pain. What is not clear, however, is whether there is a marked association between this symptom and the spinal deformity. In studies specifically exploring its prevalence in adolescents with scoliosis, the rates range considerably: from 23% to 85%.
Does the severity of the curve correlate with pain intensity?
One of main reasons for scepticism over a possible association between pain and scoliosis is the current debate in the literature on the link between the severity of the deformity and the intensity of the pain, and the association, more convincing, between pain and psychological factors (such as self-image and mental health status). Indeed, some patients with less pronounced curves showed more intense pain and vice versa, suggesting that spinal morphology is not the only factor at play.4
Some evidence from the literature suggests that the association between pain and scoliosis is not strongly linked to a biomechanical problem. Indeed, in most studies, pain did not correlate strongly with the magnitude of the curve (Cobb angle); untreated cases did reasonably well from a back pain perspective; epidemiological data revealed a much greater gender difference in scoliosis as opposed to back pain incidence; and patients’ self-image was found to be related to their pain. All these findings argue against a strong aetiological role of idiopathic scoliotic deformity in adolescent back pain.1
Does back pain in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis predispose them to pain in adulthood? What factors predispose adolescents with scoliosis to developing back pain?
In adolescents, early onset and persistence of back pain appear to be predictors of future back pain. A retrospective study showed that patients with thoracic scoliosis noted in their medical records were four times more likely to experience thoracic pain than those with no thoracic curve.5 Patients with scoliosis and back pain, compared with asymptomatic scoliosis patients, showed poorer physical function and sleep problems. Given that back pain has multiple causes, it is necessary to take into account depression, anxiety, catastrophising (i.e., having an exaggeratedly negative mindset towards actual or anticipated pain), and level of physical activity: all these factors can influence the perception and perpetuation of pain. 4,5
In conclusion
“What recent studies show is that it is crucial to evaluated the youngster’s overall health in order to correctly evaluate back pain or possible risk factors,” explains Martina Poggio. “That means not just performing a physical assessment and encouraging the patient to get regular physical exercise, but also a psychological one, evaluating their self-perception and looking for anxiety, depression and drowsiness. These factors, although they may seem secondary in a case of scoliosis, could predispose the individual to the onset of back pain. Finally, it’s important to remind youngsters and their families that current data show no clear correlation between the deformity and pain, only that some people are more predisposed to pain”.
- “Prevalence of low back pain in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review” Jean Théroux, Norman Stomski, Christopher J. Hodgetts, Ariane Ballard, Christelle Khadra, Sylvie Le May and Hubert Labelle Chiropractic & Manual Therapies (2017)
- “Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and back pain” Federico Balagué and Ferran Pellisé Scoliosis and Spinal Disorders (2016)
- “Back Pain in Children and Adolescents” Suraj Achar, Jarrod Yamanaka. Am Fam Physician (2020).
- “Back pain in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis: the contribution of morphological and psychological factors” Alisson R. Teles, · Maxime St‐Georges, · Fahad Abduljabbar, · Leonardo Simões, · Fan Jiang, Neil Saran, · Jean A. Ouellet, · Catherine E. Ferland. European Spine Journal (2020)
- “How Common Is Back Pain and What Biopsychosocial Factors Are Associated With Back Pain in Patients With Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis?” Arnold Y. L. Wong , MPhil, Dino Samartzis , Prudence W. H. Cheung, Jason Pui Yin Cheung Clin Orthop Relat Res (2019)
- “Prevalence of low back pain in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review” Jean Théroux, Norman Stomski, Christopher J. Hodgetts, Ariane Ballard, Christelle Khadra, Sylvie Le May and Hubert Labelle. Chiropractic & Manual Therapies (2017)
- “Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and back pain” Federico Balagué and Ferran Pellisé. Scoliosis and Spinal Disorders (2016)
- “Back pain in children and adolescents” Suraj Achar, Jarrod Yamanaka. American Family Physician (2020)
- “Back pain in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis: the contribution of morphological and psychological factors” Alisson R. Teles, Maxime St‐Georges, Fahad Abduljabbar, Leonardo Simões, Fan Jiang, Neil Saran, Jean A. Ouellet, Catherine E. Ferland. European Spine Journal (2020)
- “How Common Is Back Pain and What Biopsychosocial Factors Are Associated With Back Pain in Patients With Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis?” Arnold Y. L. Wong, Dino Samartzis, Prudence W. H. Cheung, Jason Pui Yin Cheung. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research (2019)